PEE Zadania egzaminacyjne: Różnice pomiędzy wersjami
Z Studia Informatyczne
Przejdź do nawigacjiPrzejdź do wyszukiwania
Nie podano opisu zmian |
Nie podano opisu zmian |
||
| Linia 9: | Linia 9: | ||
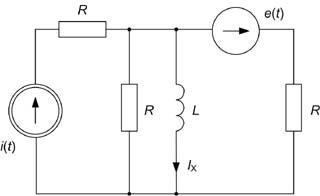
[[Grafika:PEE_Zadania_egz_zes1_1.jpg]] | [[Grafika:PEE_Zadania_egz_zes1_1.jpg]] | ||
Dane: <math>i(t)=5\sqrt{2}sin(\omega t+90^\circ)\, | Dane: <math>i(t)=5\sqrt{2}sin(\omega t+90^\circ)\,</math>, <math>e(t)=10\sqrt{2}sin(\omega t-90^\circ)\,</math>, <math>R=50\Omega</math>, <math>\omega L=3\Omega</math> | ||
<hr width="100%"> | <hr width="100%"> | ||
| Linia 19: | Linia 19: | ||
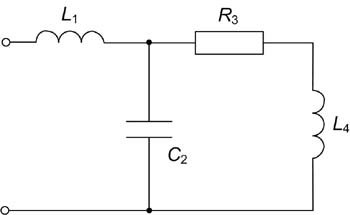
[[Grafika:PEE_Zadania_egz_zes1_2.jpg]] | [[Grafika:PEE_Zadania_egz_zes1_2.jpg]] | ||
Dane: <math>e_1(t)=50V\,</math>, <math>e_2(t)=60\sqrt{2}sin(\omega t+90^\circ)\, | Dane: <math>e_1(t)=50V\,</math>, <math>e_2(t)=60\sqrt{2}sin(\omega t+90^\circ)\,</math>, <math>R=10\Omega</math>, <math>C=0,1F\,</math> | ||
<hr width="100%"> | <hr width="100%"> | ||
Wersja z 14:08, 25 sie 2006
Zadania egzaminacyjne
Zestaw 1
Zad. 1
Obliczyć prąd w obwodzie metodą Thevenina
Dane: , , ,
Zad. 2
Obliczyć przebieg w stanie nieustalonym po przełączeniu w obwodzie
Dane: , , ,
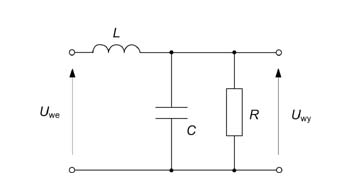
Zad. 3
Określić transmitancję napięciową, odpowiedź impulsową i charakterystyki częstotliwościowe
Dane: , ,
Zestaw 2
Zad. 1
Narysować wykres wektorowy dla obwodu
Zad. 2
Obliczyć moce elementów w obwodzie i sporządzić bilans mocy.
Dane: , , , ,
Zad. 3
Obliczyć przebieg w stanie nieustalonym po przełączeniu w obwodzie
Dane: , , , ,